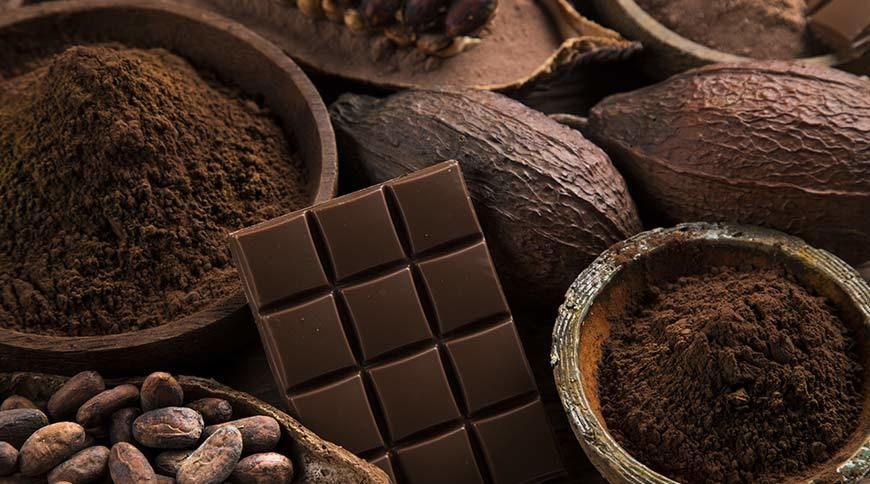
The health benefits of chocolate come directly from the cocoa, so while some might find white and milk chocolate good for the soul, it’s really the dark chocolate, with a high cocoa content, that has an abundance of health benefits.
Cocoa is rich in several antioxidants, all which contribute a variety of health benefits:
- Epicatechin and catechin: contribute to increased nitric oxide production which has a favorable impact on blood flow and heart health.
- Procyanidins: work to decrease oxidative stress, protecting cells from damage.
Chocolate also provides some essential minerals including magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, and copper which are important nutrients to support the immune system, cell production, and muscle function.
It’s important to remember that chocolate is an energy dense food and so the quantity of consumption should be considered depending on your goals. Consuming it in excess might also displace your appetite for other nutrient rich foods. For this reason, it’s best consumed after a meal or snack, as opposed to before.
While chocolate has many health benefits (due to its cocoa content), there are some factors to consider when deciding when and how much to have. These include its caffeine content, and impact on iron absorption.
- Caffeine: A dark chocolate bunny ear (30 g) contains approximately 18 mg of caffeine, similar to a cup of green tea. For those who find caffeine has a stimulating effect, this could be enough to delay sleep if consumed later in the afternoon or evening. For this reason, having earlier in the day might be better placed.
- Iron absorption: Chocolate contains oxalates and polyphenols which reduce the absorption of non haem (plant based) iron. Therefore, if you have a history of low iron, it is best to avoid having chocolate at the same time as meals or snacks containing non haem iron foods (nuts, seeds, tofu, beans, fortified cereals).
Top Tips
Our tips to help you reap the benefits of chocolate and prevent a chocolate coma this Easter.
1. Go for quality over quantity
2. Savour your chocolate
3. Portion it out
4. Eat it after a meal or snack, not before
5. If caffeine effects your sleep, avoid having too much in the evening
Did you know?
Cocoa and Cacao are different!
Cacao is the raw, unprocessed bean, compared to cocoa which is roasted.
In the raw form, cacao contains more minerals, antioxidants, and caffeine than cocoa. Cacao does have a slightly stronger and more bitter taste, so can take some getting use to.
You can often find it in raw chocolate bars or as cacao powder. Give it a try and see if you can taste the difference!